Sweden officially joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization Thursday, a historic shift that highlights how Russian President Vladimir Putin’s war in Ukraine is transforming European security in ways he may not have foreseen.
Sweden finally joins NATO in expansion spurred by Putin’s Ukraine war
To justify his aggression in Ukraine, Putin cited the possibility of NATO expansion. Now, in one of the conflict’s many twists, his war has brought a bigger, stronger alliance to his door. Russia will have to live with the consequences for years.
The addition of Sweden and Finland will strengthen NATO in the far north, where Russia keeps much of it second-strike capability, and boost its presence around the Baltic Sea, particularly around the Russian exclave of Kaliningrad.
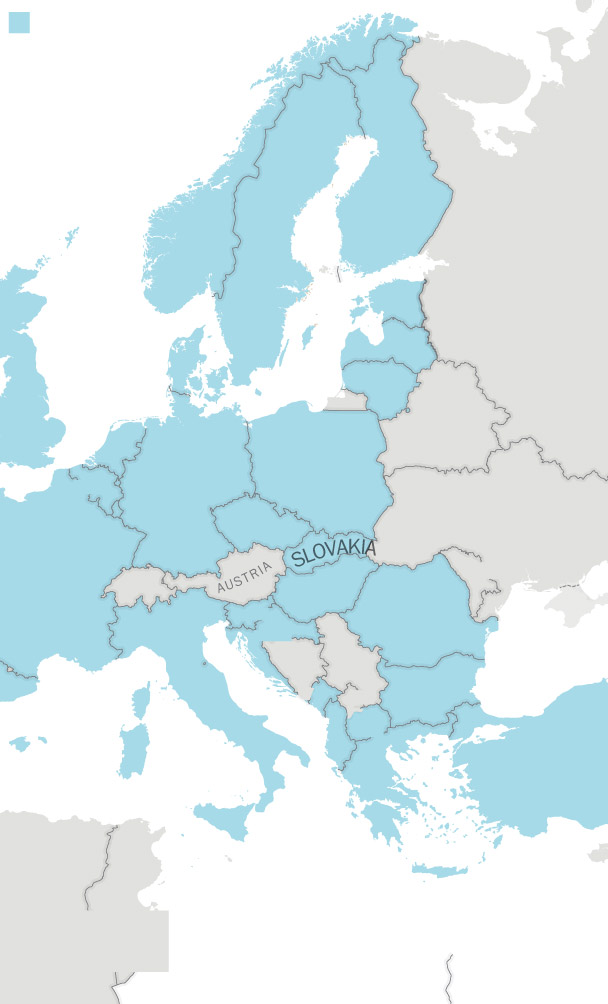
NATO member countries
Atlantic
Ocean
FINLAND
NORWAY
RUSSIA
EST.
North
Sea
SWEDEN
LAT.
DEN.
LITH.
RUS.
U.K.
BELARUS
NETH.
POLAND
GERMANY
BELG.
LUX.
UKRAINE
CZECH.
REP.
FRANCE
MOLDOVA
HUNG.
SWITZ.
Crimea
SLOV.
ROM.
Illegally annexed by Russia in March 2014
CROATIA
BOS.
SERBIA
BULG.
ITALY
MONT.
KOS.
SPAIN
NORTH
MAC.
ALB.
TURKEY
GREECE
Mediterranean
Sea
400 MILES
NATO countries not shown:
Portugal, Iceland, United States and Canada
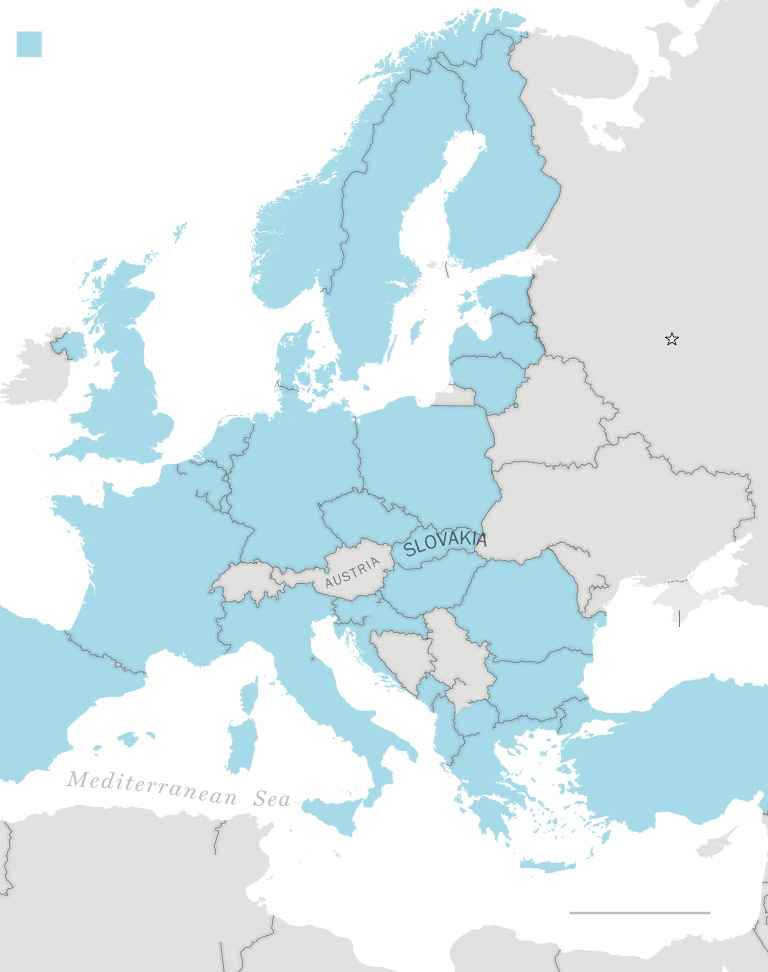
NATO member countries
Atlantic
Ocean
FINLAND
NORWAY
RUSSIA
EST.
SWEDEN
North
Sea
Moscow
LAT.
DEN.
LITH.
RUS.
UNITED
KINGDOM
BELARUS
NETH.
GERMANY
POLAND
BELG.
LUX.
UKRAINE
CZECH.
REP.
FRANCE
MOLDOVA
SWITZ.
HUNGARY
Crimea
SLOV.
ROMANIA
ITALY
Illegally annexed by Russia in March 2014
CROATIA
BOS.
SERBIA
SPAIN
BULGARIA
KOS.
MONT.
NORTH
MAC.
ALB.
TURKEY
GREECE
NATO countries not shown:
Portugal, Iceland, United States and Canada
400 MILES
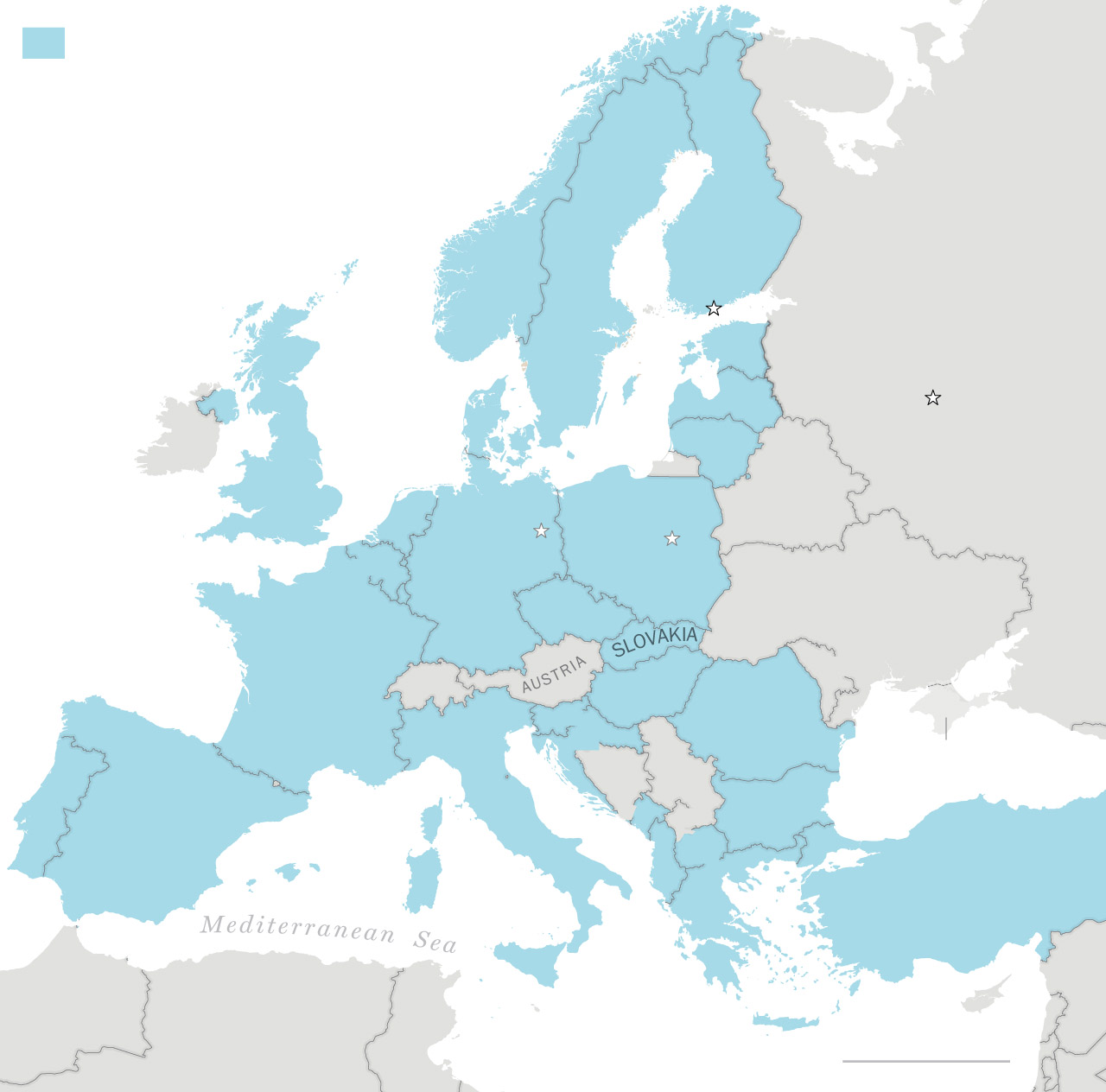
NATO member countries
NATO countries not shown:
Iceland, United States and Canada
FINLAND
NORWAY
Atlantic
Ocean
RUSSIA
Helsinki
ESTONIA
SWEDEN
North
Sea
Moscow
LATVIA
DEN.
LITHUANIA
IRELAND
UNITED
KINGDOM
RUS.
BELARUS
Berlin
NETH.
Warsaw
GERMANY
POLAND
BELG.
LUX.
UKRAINE
CZECH.
REP.
FRANCE
MOLDOVA
SWITZ.
HUNGARY
Crimea
SLOV.
ROMANIA
CROATIA
Illegally annexed by Russia in March 2014
PORTUGAL
BOS.
SERBIA
SPAIN
BULGARIA
ITALY
MONT.
KOS.
NORTH
MAC.
ALB.
TURKEY
GREECE
400 MILES
Sweden’s navy has experience operating in — and under — Baltic waters, and its fighter jets will patrol the region’s skies, making it easier for NATO to supply or defend Baltic allies, should the need arise. Stockholm has already said it will send troops to join a multinational force based in Latvia.
“Sweden is a strong democracy with a highly capable military that shares our values and vision for the world,” the White House said in a briefing statement on Thursday. “Having Sweden as a NATO Ally will make the United States and our Allies even safer.”
Although Sweden’s NATO bid was blocked at various points by Turkey, and then by Hungary, the fact that it made it in sends an important signal to Putin as he wages war in Ukraine and threatens other neighbors, said Anna Wieslander, director for Northern Europe at the Atlantic Council.
That message: “That he cannot dictate, and if he does, there will be pushback.”
Russia did not immediately comment on the news. The country’s response to Finnish membership was muted, though Russian officials have talked in general terms about the need to adjust their military posture in response to NATO’s new borders and plans.
A few years ago, it would have been difficult to imagine Sweden joining NATO. Military nonalignment was a part of the country’s identity.
But Russia’s February 2022 invasion seemed to rouse Europe from a post-Cold War slumber, spurring deep changes in how the region’s relatively wealthy democracies think about their own security.
The European Union began the process of weaning itself of Russian oil and gas. It dug into its stockpiles to send weapons to Ukraine. And it has started to step up defense spending — albeit more slowly than many at NATO headquarters or in Washington might like.
NATO, meanwhile, began its biggest overhaul since the Cold War, drawing up new battle plans that are more squarely focused on deterring Russia and defending every inch of NATO territory from day one should Moscow try anything.
When Russian tanks rolled on Kyiv, Finnish sentiment on NATO shifted quickly. Sweden took slightly longer to come around, but applied for membership alongside its neighbor in May 2022.
Both countries — and much of the alliance — expected a smooth process. But approving newcomers requires unanimity, and it soon became clear that Turkey would object at every step.
What followed was more than 20 months of obstruction and delay from Turkey, followed by stalling from Hungary — with public feuding that no doubt pleased Putin.
When it became clear that Turkey’s problem was with Finland, not Sweden, their bids were split. Finland joined last spring, while Sweden kept negotiating.
Turkish president Recep Tayyip Erdogan sought F-16 fighter jets from the United States and insisted that Sweden crack down on groups Turkey considers to be terrorists. Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban pressed Sweden’s prime minister to pay a visit to Budapest and cut deal to get more Swedish-built fighter jets.
In the end, after much drama and fraught diplomacy, both countries extracted what they could and agreed to welcome another new member.
The Swedish flag will not rise outside NATO’s Brussels headquarters until Monday, officials said, but NATO’s key protection — the collective defense clause known as “Article 5” — goes into effect immediately.
“We will go to sleep here tonight with Article 5 embracing this country,” said Wieslander of the Atlantic Council, in a phone call from Sweden. “That is a huge shift for us.”